Class: AP2 | Unit: Unit 5 | Updated: 2026-02-09
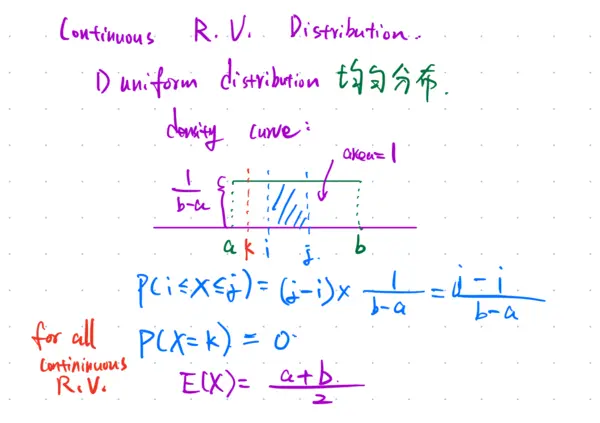
Continuous R.V. Distribution.1) uniform distribution 均匀分布Density curve:area=1$1/(b-a)$a k i j b$P(i \le X \le j) = (j-i) \times 1/(b-a) = (j-i)/(b-a)$for all Continuous R.V. $P(X=k) = 0$.$E(X) = (a+b)/2$For Continuous Random Variable.possible outcomes is infinite.Need to use geometric probability model.Need to calc the area of event.2) Normal distribution.density curve.Symmetric bell-shaped.$X \sim N(\mu_X, \sigma_X)$.$P(a \le X \le b) = \text{normalcdf}(\text{lower: a, upper: b, } \mu: \mu_X, \sigma: \sigma_X)$Central Limit Theorem (中心极限定理)When $Y = X_1 + X_2 + ... + X_n$.1) assume all $X_i$ are independent and identically distributed.When $n \ge 30$, $Y \sim N$.$E(Y) = E(X_1 + X_2 + ... + X_n) = E(X_1) + E(X_2) + ... + E(X_n) = nE(X)$Std$(Y) = \text{std}(X_1 + ... + X_n) = \sqrt{\text{std}^2(X_1) + ... + \text{std}^2(X_n)} = \sqrt{n \text{std}^2(X)} = \sqrt{n} \text{std}(X)$Note:$E(aX+bY+cZ+d) = aE(X)+bE(Y)+cE(Z)+d$Std$(aX+bY+cZ+d) = \sqrt{a^2 \text{std}^2(X) + b^2 \text{std}^2(Y) + c^2 \text{std}^2(Z)}$ (assuming X,Y,Z are independent)Note:PDF of Normal distribution: $f(x) = \frac{1}{\sigma \sqrt{2\pi}} e^{-\frac{1}{2}(\frac{x-\mu}{\sigma})^2}$$\mu$: mean of normal distribution$\sigma$: std of normal distributionWhen $Y = X_1 + ... + X_n$ (sample).If $Y \sim N$, $E(Y)=nE(X)$, Std$(Y)=\sqrt{n} \text{std}(X)$.Sample mean: $\bar{X} = (X_1 + ... + X_n) / n$.If $Y \sim N$, then $\bar{X} \sim N$.$E(\bar{X}) = E(Y/n) = (1/n)E(Y) = (1/n) nE(X) = E(X)$ (center of sample mean)Std$(\bar{X}) = \text{std}(Y/n) = (1/n)\text{std}(Y) = (1/n)\sqrt{n}\text{std}(X) = \text{std}(X)/\sqrt{n}$Std$(\bar{X}) = \text{std}(X)/\sqrt{n}$